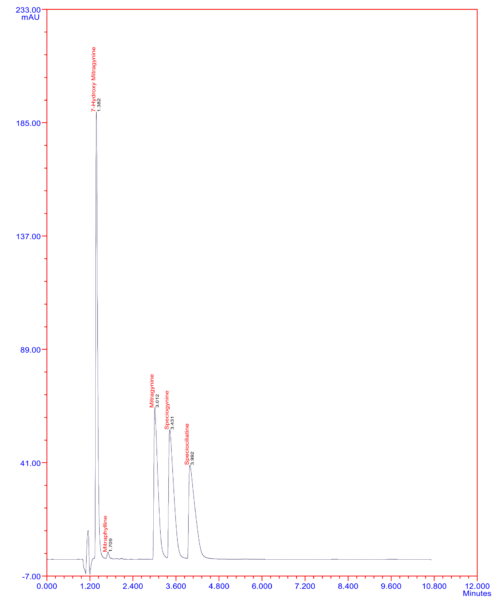
5 mitragyna alkaloids
7-Hydroxy Mitragynine
Mitraphylline
Mitragynine
Speciogynine
Speciociliatine
Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) is a tropical evergreen tree native to Southeast Asia, primarily found in countries such as Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Papua New Guinea. The leaves of the kratom tree have been used for centuries in traditional medicine and cultural practices in the region.
The active compounds in kratom are mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, which interact with opioid receptors in the brain. This gives kratom its unique properties, including pain relief, mood enhancement, and stimulation at lower doses, and sedation at higher doses. While kratom has been used traditionally for various purposes, it has gained attention in recent years in Western countries as an alternative or complementary remedy for pain management and opioid withdrawal symptoms.
Kratom is often consumed in the form of dried leaves, powdered leaves, or extracts. It can be brewed as a tea, consumed in capsules, or simply ingested by mixing the powder with water. The effects can vary depending on the strain and dosage. There are different strains of kratom, such as Bali, Maeng Da, Borneo, and Malay, each with its unique characteristics and potential benefits.
Despite its potential therapeutic uses, kratom has also been a subject of controversy and concern. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued warnings about the potential risks associated with kratom, including addiction, abuse, and adverse effects on health. Some users have reported side effects such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, and increased heart rate.